
Very wealthy people frequently invest in things like gold, real estate, land, private and commercial, and even art pieces. Real estate continues to be a common asset class in their portfolios to counteract the volatility of stocks. Types of assets classes is based on the existence of assets in physical form, or it lacks physical substance. The different type of assets classes for an organization or an individual is an important which of the following items are plant assets? factor to understand if they intend to manage their finances efficiently. Get stock recommendations, portfolio guidance, and more from The Motley Fool’s premium services.
Types Of Assets In Accounting

The types of assets in accounting is based on usage, i.e., either assets are used in day-to-day business operations or accumulated for some specific purpose. Regardless of the company you’re analyzing, plant assets tend to be those held for long-term use and depreciated over their useful lives. As time goes on, plant assets wear down and must be replaced, although most companies try to extend useful life for as long as possible. Current assets typically include cash, inventory, accounts receivable, and other short-term liquid assets. In contrast, plant assets represent long-term property expected to be around for at least a year, often quite a bit longer than that. This type of accounting asset is used in every necessary business operation, i.e., from production to sales—E.g.
Struggling with Financial Accounting?
These are considered measurable assets because their value can be easily identified based on their current condition and expected future benefits. Tangible assets include current assets like cash, inventory, marketable securities, etc., and noncurrent assets like property, plant, equipment, etc. Depreciation is the process by which a plant asset experiences wear and tear over a particular period of time. Depreciation expense — calculated in several different ways — is then carried through to the income statement and reduces net income. Over time, plant asset values are also reduced by depreciation on the balance sheet. Like any category of assets, it’s critical to evaluate plant assets on a company-by-company basis.
Chegg Products & Services
Needless to say, they’re an enormously important part of producing goods and/or services in an economically efficient manner. Businesses must be especially careful in making these investments since buildings and land are immovable https://www.hotelmareblusalento.com/frequently-asked-questions-about-proadvisor-2/ and can’t be easily substituted. Depending on the industry, plant assets may make up either a very substantial percentage of total assets, or they may make up only a small part.

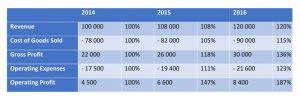
Understanding the types of accounting assets helps place the correct assets in their respective asset blocks. In addition, the knowledge helps create an accurate positional statement for the company. Assets are the resources owned by individuals, companies, or governments expected to generate future cash flows over a long period. Plant assets are usually expensive, long-term investments made to underpin a company’s production process.
Current assets versus plant assets

Founded in 1993, The Motley Fool is a financial services company dedicated to making the world smarter, happier, and richer. The Motley Fool reaches millions of people every month through our premium investing solutions, free guidance and market analysis on Fool.com, top-rated podcasts, and non-profit The Motley Fool Foundation. An asset’s “useful life” is an accounting estimate of how long it will probably be used to generate income at a reasonable cost.
- While they’re most definitely both considered part of the asset category, current assets and plant assets don’t share all that much in common.
- Depreciation is the process by which a plant asset experiences wear and tear over a particular period of time.
- This type of accounting asset is used in every necessary business operation, i.e., from production to sales—E.g.
- Like any category of assets, it’s critical to evaluate plant assets on a company-by-company basis.
- Here, we’ll discuss what plant assets are, why they matter, and how they fit into a company’s financial circumstances.
Company
- From an accounting perspective, plant assets are typically held on the balance sheet at historical cost (what the company paid for them) less depreciation (ongoing wear-and-tear expense) over time.
- The location, intended usage, and current condition of any alterations will all be known to the staff.
- I.e., these assets generate income but have negligible participation in the basic functionality of a business.
- Types of assets classes is based on the existence of assets in physical form, or it lacks physical substance.
- Founded in 1993, The Motley Fool is a financial services company dedicated to making the world smarter, happier, and richer.
Industries like heavy shipping or oil extraction stand to employ a greater percentage of plant assets than industries like software, in which teams may be remote and sometimes globally distributed. With asset management, businesses of all sizes and in all industries can easily keep track of their assets, QuickBooks whether liquid or fixed. The location, intended usage, and current condition of any alterations will all be known to the staff.
In the end, be careful to distinguish between asset types both on the balance sheet and in practice. Here’s an overview of GE Vernova’s business and whether the stock would benefit investors’ portfolios.
Generally, plant assets are among the most valuable company assets and tend to be relied on greatly over the long term. As such, these assets provide an economic benefit for a significant period of time. From an accounting perspective, plant assets are typically held on the balance sheet at historical cost (what the company paid for them) less depreciation (ongoing wear-and-tear expense) over time. This can help provide accurate financial information if the market for plant assets is unusually volatile. This type of accounting asset is not meant to be applied in day-to-day business operations but is accumulated as future investments or contingent situations.
Based on Physical Existence
I.e., these assets generate income but have negligible participation in the basic functionality of a business. E.g., Land purchased to develop a new building for head office, or shares purchased considering future price appreciation. In most cases, you’ll find that expensive, valuable assets tend to fall into the plant asset category, while shorter-term assets meant to be used in the normal course of business fall into the current asset category. While they’re most definitely both considered part of the asset category, current assets and plant assets don’t share all that much in common. Plant assets are key to a company’s production process and are often considered among the most valuable items on the balance sheet. Here, we’ll discuss what plant assets are, why they matter, and how they fit into a company’s financial circumstances.
